Elasticsearch 热-温-冷数据架构
更新时间:2024-03-07 19:06:53
PDF
在某些大规模数据分析场景(比如时间数据分析),可以采用此架构:基于时间创建 index,然后持续地把温/冷数据迁移到相应的数据节点。详情可参考官方博客 “Hot-Warm” Architecture in Elasticsearch 5.x。
节点介绍
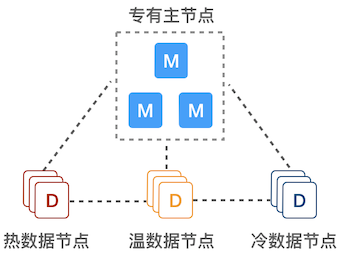
-
专有主节点:由于不保存数据,也就不参与索引和查询操作,不会被长 GC 干扰,负载可以保持在较低水平,能极大提高集群的稳定性。
-
热数据节点:保存近期的 index,承担最频繁的写入和查询操作,可以配置较高的资源,如超高性能主机及硬盘。可以在集群配置参数里 Elasticsearch 节点的参数 node.attr.data(热)做修改,默认为
hot。 -
温/冷数据节点:保存只读 index,会接收少量的查询请求,可以配置较低的资源。可以在集群配置参数里 Elasticsearch 节点的参数 node.attr.data(温)和 node.attr.data(冷)做修改,默认为
warm和cold。
节点配置
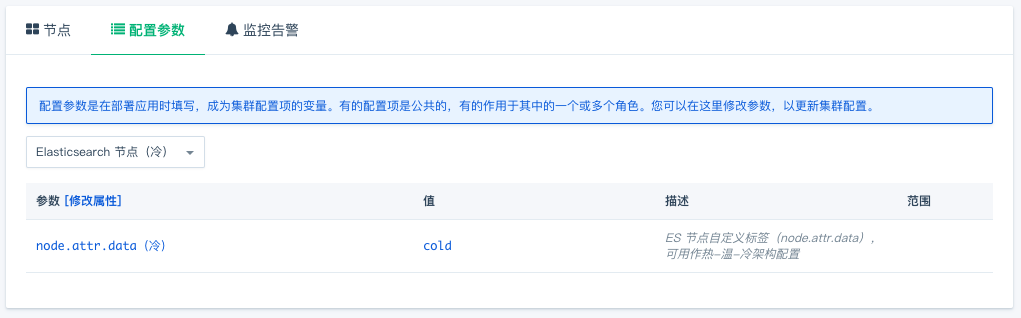
创建好的集群如下图所示。
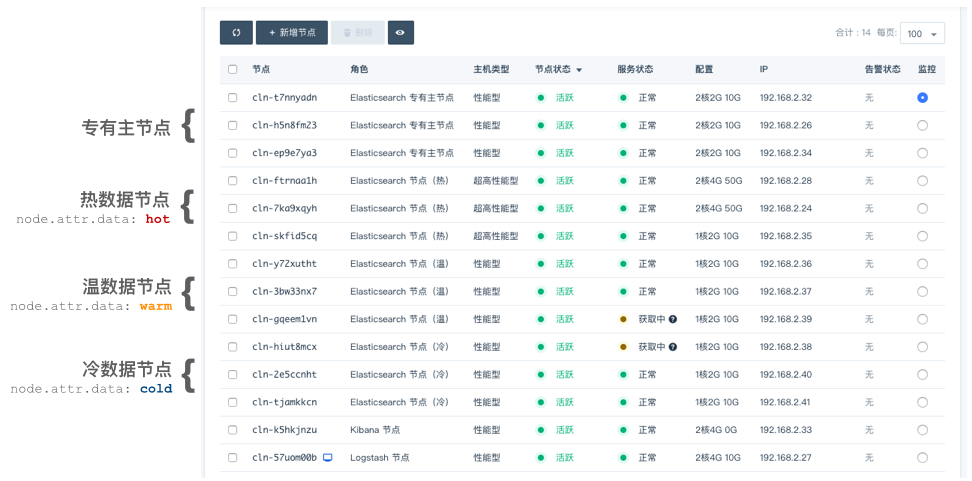
如下图所示,假设有三个 index,分别代表热、温、冷 index 数据,它们最初都处于热数据节点上:
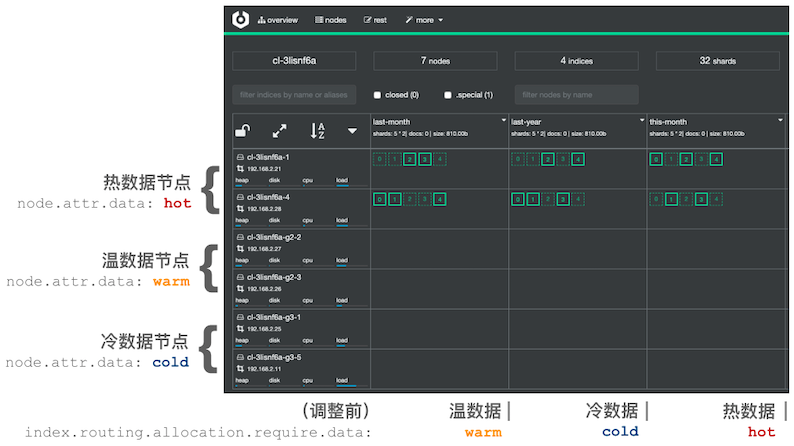
可以使用如下命令迁移温数据(名为 last-month 的 index,可根据实际情况选择相应的 index)到相应节点上。
PUT /last-month/_settings
{
"index.routing.allocation.require.data": "warm"
}使用如下命令迁移冷数据(名为 last-year 的 index,可根据实际情况选择相应的 index):
PUT /last-year/_settings
{
"index.routing.allocation.require.data": "cold"
}下面的动态截屏展示了通过 Kibana 的 Dev Tools 进行温/冷数据迁移的过程: